View 焦点处理
目录
[TOC]
按键事件处理
android.view.ViewRootImpl$ViewPostImeInputStage.processKeyEvent(ViewRootImpl.java:4102)
at android.view.ViewRootImpl$ViewPostImeInputStage.onProcess(ViewRootImpl.java:4000)
at android.view.ViewRootImpl$InputStage.deliver(ViewRootImpl.java:3562)
at android.view.ViewRootImpl$InputStage.onDeliverToNext(ViewRootImpl.java:3615)
at android.view.ViewRootImpl$InputStage.forward(ViewRootImpl.java:3581)
at android.view.ViewRootImpl$AsyncInputStage.forward(ViewRootImpl.java:3698)
at android.view.ViewRootImpl$InputStage.apply(ViewRootImpl.java:3589)
at android.view.ViewRootImpl$AsyncInputStage.apply(ViewRootImpl.java:3755)
at android.view.ViewRootImpl$InputStage.deliver(ViewRootImpl.java:3562)
at android.view.ViewRootImpl$InputStage.onDeliverToNext(ViewRootImpl.java:3615)
at android.view.ViewRootImpl$InputStage.forward(ViewRootImpl.java:3581)
at android.view.ViewRootImpl$InputStage.apply(ViewRootImpl.java:3589)
at android.view.ViewRootImpl$InputStage.deliver(ViewRootImpl.java:3562)
at android.view.ViewRootImpl$InputStage.onDeliverToNext(ViewRootImpl.java:3615)
at android.view.ViewRootImpl$InputStage.forward(ViewRootImpl.java:3581)
at android.view.ViewRootImpl$AsyncInputStage.forward(ViewRootImpl.java:3731)
at android.view.ViewRootImpl$ImeInputStage.onFinishedInputEvent(ViewRootImpl.java:3892)
at android.view.inputmethod.InputMethodManager$PendingEvent.run(InputMethodManager.java:2208)
at android.view.inputmethod.InputMethodManager.invokeFinishedInputEventCallback
(InputMethodManager.java:1849)
at android.view.inputmethod.InputMethodManager.finishedInputEvent(InputMethodManager.java:1840)
at android.view.inputmethod.InputMethodManager$ImeInputEventSender.onInputEventFinished
(InputMethodManager.java:2185)
at android.view.InputEventSender.dispatchInputEventFinished(InputEventSender.java:141)
at android.os.MessageQueue.nativePollOnce(
Native Method)
从上面的堆栈信息可以看出是从InputEventSender.dispatchInputEventFinished调用到ViewRootImpl$ViewPostImeInputStage.processKeyEvent,而dispatchInputEventFinished是从native调上来,不做分析。
frameworks\base\core\java\android\view\InputEventSender.java
// Called from native code.
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
private void dispatchInputEventFinished(int seq, boolean handled) {
onInputEventFinished(seq, handled);
}
从ViewRootImpl的processKeyEvent开始分析按键事件,ViewRootImpl$ViewPostImeInputStage.processKeyEvent源代码:
private int processKeyEvent(QueuedInputEvent q) {
final KeyEvent event = (KeyEvent)q.mEvent;
if (event.getAction() != KeyEvent.ACTION_UP) {
// If delivering a new key event, make sure the window is
// now allowed to start updating.
handleDispatchDoneAnimating();
}
// Deliver the key to the view hierarchy.
if (mView.dispatchKeyEvent(event)) {
return FINISH_HANDLED;
}
if (shouldDropInputEvent(q)) {
return FINISH_NOT_HANDLED;
}
// If the Control modifier is held, try to interpret the key as a shortcut.
if (event.getAction() == KeyEvent.ACTION_DOWN
&& event.isCtrlPressed()
&& event.getRepeatCount() == 0
&& !KeyEvent.isModifierKey(event.getKeyCode())) {
if (mView.dispatchKeyShortcutEvent(event)) {
return FINISH_HANDLED;
}
if (shouldDropInputEvent(q)) {
return FINISH_NOT_HANDLED;
}
}
// Apply the fallback event policy.
if (mFallbackEventHandler.dispatchKeyEvent(event)) {
return FINISH_HANDLED;
}
if (shouldDropInputEvent(q)) {
return FINISH_NOT_HANDLED;
}
// Handle automatic focus changes.
if (event.getAction() == KeyEvent.ACTION_DOWN) {
int direction = 0;
switch (event.getKeyCode()) {
case KeyEvent.KEYCODE_DPAD_LEFT:
if (event.hasNoModifiers()) {
direction = View.FOCUS_LEFT;
}
break;
case KeyEvent.KEYCODE_DPAD_RIGHT:
if (event.hasNoModifiers()) {
direction = View.FOCUS_RIGHT;
}
break;
case KeyEvent.KEYCODE_DPAD_UP:
if (event.hasNoModifiers()) {
direction = View.FOCUS_UP;
}
break;
case KeyEvent.KEYCODE_DPAD_DOWN:
if (event.hasNoModifiers()) {
direction = View.FOCUS_DOWN;
}
break;
case KeyEvent.KEYCODE_TAB:
if (event.hasNoModifiers()) {
direction = View.FOCUS_FORWARD;
} else if (event.hasModifiers(KeyEvent.META_SHIFT_ON)) {
direction = View.FOCUS_BACKWARD;
}
break;
}
if (direction != 0) {
View focused = mView.findFocus();
if (focused != null) {
View v = focused.focusSearch(direction);
if (v != null && v != focused) {
// do the math the get the interesting rect
// of previous focused into the coord system of
// newly focused view
focused.getFocusedRect(mTempRect);
if (mView instanceof ViewGroup) {
((ViewGroup) mView).offsetDescendantRectToMyCoords(
focused, mTempRect);
((ViewGroup) mView).offsetRectIntoDescendantCoords(
v, mTempRect);
}
if (v.requestFocus(direction, mTempRect)) {
playSoundEffect(SoundEffectConstants
.getContantForFocusDirection(direction));
return FINISH_HANDLED;
}
}
// Give the focused view a last chance to handle the dpad key.
if (mView.dispatchUnhandledMove(focused, direction)) {
return FINISH_HANDLED;
}
} else {
// find the best view to give focus to in this non-touch-mode with no-focus
View v = focusSearch(null, direction);
if (v != null && v.requestFocus(direction)) {
return FINISH_HANDLED;
}
}
}
}
return FORWARD;
}
从上面代码可以看出两块逻辑:
-
首先由dispatchKeyEvent进行按键事件的分发,如果dispatchKeyEvent方法返回true,则按键事件被消费不继续处理。
-
如果dispatchKeyEvent方法返回false,则针对上下左右键进行焦点切换,从而实现通过按键控制界面。(这块就是android上下左右键操作的默认实现,以后就不会感觉很神秘了)
按键事件分发dispatchKeyEvent
从上面代码可以看出是从mView开始按键事件分发:
// Deliver the key to the view hierarchy.
if (mView.dispatchKeyEvent(event)) {
return FINISH_HANDLED;
}
mView这里是Activity的顶层容器DecorView,它是一FrameLayout,所以这里的dispatchKeyEvent方法应执行的是ViewGroup的dispatchKeyEvent()方法。 (此处有误,DecorView的ispatchKeyEvent有重写,会先调用Activity的ispatchKeyEvent方法)
ViewGroup的dispatchKeyEvent()方法的源码如下:
@Override
public boolean dispatchKeyEvent(KeyEvent event) {
if (mInputEventConsistencyVerifier != null) {
mInputEventConsistencyVerifier.onKeyEvent(event, 1);
}
if ((mPrivateFlags & (PFLAG_FOCUSED | PFLAG_HAS_BOUNDS))
== (PFLAG_FOCUSED | PFLAG_HAS_BOUNDS)) {
if (super.dispatchKeyEvent(event)) {
return true;
}
} else if (mFocused != null && (mFocused.mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_HAS_BOUNDS)
== PFLAG_HAS_BOUNDS) {
if (mFocused.dispatchKeyEvent(event)) {
return true;
}
}
if (mInputEventConsistencyVerifier != null) {
mInputEventConsistencyVerifier.onUnhandledEvent(event, 1);
}
return false;
}
从上面的源码可以看出: 如果当前viewGroup获取了焦点则直接调用父类的dispatchKeyEvent,如果父类的dispatchKeyEvent方法返回true,则返回true,表示消费了该按键事件,那么按键事件就不会往下进行分发。
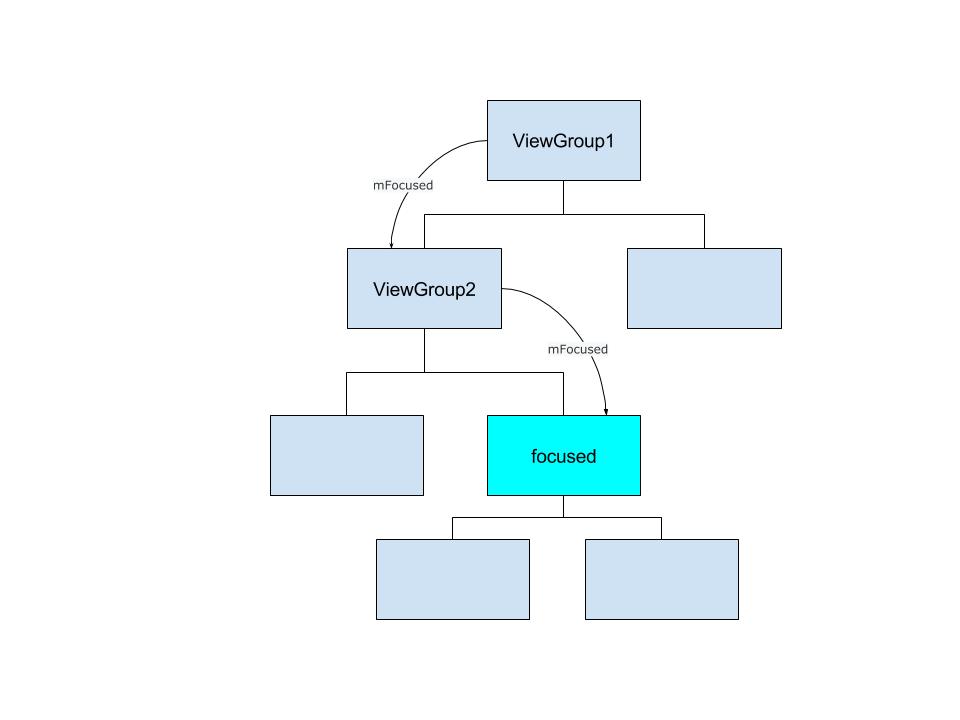
如果viewGroup自己不消耗按键事件则传给ViewGroup 的 mFocused进行按键事件分发。mFocused 源码解释为: The view contained within this ViewGroup that has or contains focus. 即mFocused是获取了焦点的view或包含了焦点View的ViewGroup。
上面函数可以概括为:把按键事件一层一层分发给当前获取焦点的View处理。
OnKeyListener.onKey
按键通过层层分发,最终交给当前获取焦点的View处理,如果是ViewGroup,则调用super.dispatchKeyEvent(event)即最终会调用view.dispatchKeyEvent,如果是View则直接调用view.dispatchKeyEvent,其源码如下:
public boolean dispatchKeyEvent(KeyEvent event) {
if (mInputEventConsistencyVerifier != null) {
mInputEventConsistencyVerifier.onKeyEvent(event, 0);
}
// Give any attached key listener a first crack at the event.
//noinspection SimplifiableIfStatement
ListenerInfo li = mListenerInfo;
if (li != null && li.mOnKeyListener != null && (mViewFlags & ENABLED_MASK) == ENABLED
&& li.mOnKeyListener.onKey(this, event.getKeyCode(), event)) {
return true;
}
if (event.dispatch(this, mAttachInfo != null
? mAttachInfo.mKeyDispatchState : null, this)) {
return true;
}
if (mInputEventConsistencyVerifier != null) {
mInputEventConsistencyVerifier.onUnhandledEvent(event, 0);
}
return false;
}
Event.Callback
从上面代码可以看出是优先调用mOnKeyListener.onKey方法,如果onkey方法返回false才调用event.dispatch。event.dispatch第一个参数为Event.Callback接口:
public interface Callback {
/**
* Called when a key down event has occurred. If you return true,
* you can first call {@link KeyEvent#startTracking()
* KeyEvent.startTracking()} to have the framework track the event
* through its {@link #onKeyUp(int, KeyEvent)} and also call your
* {@link #onKeyLongPress(int, KeyEvent)} if it occurs.
*
* @param keyCode The value in event.getKeyCode().
* @param event Description of the key event.
*
* @return If you handled the event, return true. If you want to allow
* the event to be handled by the next receiver, return false.
*/
boolean onKeyDown(int keyCode, KeyEvent event);
/**
* Called when a long press has occurred. If you return true,
* the final key up will have {@link KeyEvent#FLAG_CANCELED} and
* {@link KeyEvent#FLAG_CANCELED_LONG_PRESS} set. Note that in
* order to receive this callback, someone in the event change
* <em>must</em> return true from {@link #onKeyDown} <em>and</em>
* call {@link KeyEvent#startTracking()} on the event.
*
* @param keyCode The value in event.getKeyCode().
* @param event Description of the key event.
*
* @return If you handled the event, return true. If you want to allow
* the event to be handled by the next receiver, return false.
*/
boolean onKeyLongPress(int keyCode, KeyEvent event);
/**
* Called when a key up event has occurred.
*
* @param keyCode The value in event.getKeyCode().
* @param event Description of the key event.
*
* @return If you handled the event, return true. If you want to allow
* the event to be handled by the next receiver, return false.
*/
boolean onKeyUp(int keyCode, KeyEvent event);
/**
* Called when multiple down/up pairs of the same key have occurred
* in a row.
*
* @param keyCode The value in event.getKeyCode().
* @param count Number of pairs as returned by event.getRepeatCount().
* @param event Description of the key event.
*
* @return If you handled the event, return true. If you want to allow
* the event to be handled by the next receiver, return false.
*/
boolean onKeyMultiple(int keyCode, int count, KeyEvent event);
}
View实现了Event.Callback接口。
综合以上分析可以看出:按键事件通过一层层dispatchKeyEvent分发传给当前获取焦点的View处理,最后获取焦点的View执行优先级是OnKeyListener.onKey > onKeyDown(onKeyUp)
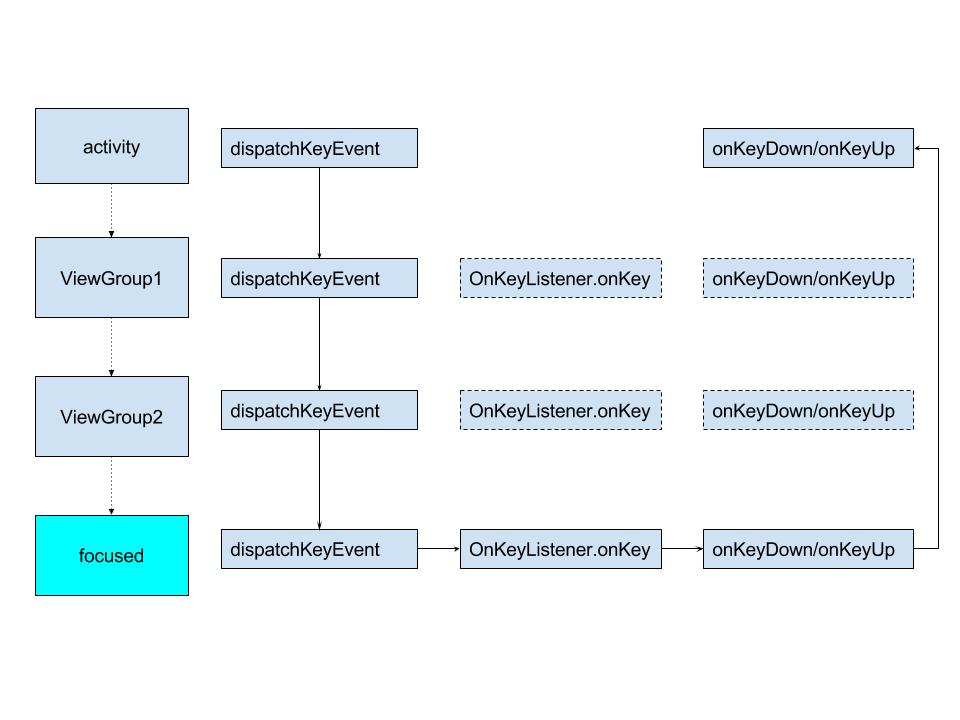
默认上下左右键实现
如果上面按键分发流程dispatchKeyEvent返回false,则android会针对按下事件,对上下左右键及TAB进行处理,实现默认的焦点切换功能。
按键转换为方向
首先将按键转换成对应方向值direction,上下左右及前后
int direction = 0;
switch (event.getKeyCode()) {
case KeyEvent.KEYCODE_DPAD_LEFT:
if (event.hasNoModifiers()) {
direction = View.FOCUS_LEFT;
}
break;
case KeyEvent.KEYCODE_DPAD_RIGHT:
if (event.hasNoModifiers()) {
direction = View.FOCUS_RIGHT;
}
break;
case KeyEvent.KEYCODE_DPAD_UP:
if (event.hasNoModifiers()) {
direction = View.FOCUS_UP;
}
break;
case KeyEvent.KEYCODE_DPAD_DOWN:
if (event.hasNoModifiers()) {
direction = View.FOCUS_DOWN;
}
break;
case KeyEvent.KEYCODE_TAB:
if (event.hasNoModifiers()) {
direction = View.FOCUS_FORWARD;
} else if (event.hasModifiers(KeyEvent.META_SHIFT_ON)) {
direction = View.FOCUS_BACKWARD;
}
break;
}
根据当前的焦点状态,查找下一个将要获取焦点的View,然后通过view.requestFocus获取焦点。
如果当前已有view获取焦点focused,则根据当前focused View和方向direction找到下一个将获取焦点的View。
View focused = mView.findFocus();
if (focused != null) {
View v = focused.focusSearch(direction);
if (v != null && v != focused) {
// do the math the get the interesting rect
// of previous focused into the coord system of
// newly focused view
focused.getFocusedRect(mTempRect);
if (mView instanceof ViewGroup) {
((ViewGroup) mView).offsetDescendantRectToMyCoords(
focused, mTempRect);
((ViewGroup) mView).offsetRectIntoDescendantCoords(
v, mTempRect);
}
if (v.requestFocus(direction, mTempRect)) {
playSoundEffect(SoundEffectConstants
.getContantForFocusDirection(direction));
return FINISH_HANDLED;
}
}
// Give the focused view a last chance to handle the dpad key.
if (mView.dispatchUnhandledMove(focused, direction)) {
return FINISH_HANDLED;
}
}
如果当前没有View获取焦点,则根据方向查找下一个view,见else部分代码:
else {
// find the best view to give focus to in this non-touch-mode with no-focus
View v = focusSearch(null, direction);
if (v != null && v.requestFocus(direction)) {
return FINISH_HANDLED;
}
}
获取当前焦点View
查找当前获取焦点的View,这里调用mView即ViewGroup的findFocus:
public View findFocus() {
if (DBG) {
System.out.println("Find focus in " + this + ": flags="
+ isFocused() + ", child=" + mFocused);
}
if (isFocused()) {
return this;
}
if (mFocused != null) {
return mFocused.findFocus();
}
return null;
}
如果当前view获取焦点则返回自己,否则向下一级View 继续查找,最终调用View的findFocus:
public View findFocus() {
return (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_FOCUSED) != 0 ? this : null;
}
寻找下一个焦点View
找到当前focused后,调用focused.focusSearch(direction)寻找下一个view。
ViewGroup.focusSearch:
public View focusSearch(View focused, int direction) {
if (isRootNamespace()) {
// root namespace means we should consider ourselves the top of the
// tree for focus searching; otherwise we could be focus searching
// into other tabs. see LocalActivityManager and TabHost for more info
return FocusFinder.getInstance().findNextFocus(this, focused, direction);
} else if (mParent != null) {
return mParent.focusSearch(focused, direction);
}
return null;
}
View.focusSearch:
public View focusSearch(@FocusRealDirection int direction) {
if (mParent != null) {
return mParent.focusSearch(this, direction);
} else {
return null;
}
}
以上两个函数实现可以看出都是交给parent去查找,直到是isRootNamespace()的顶层布局才开始真正的查找。查找算法交给了FocusFinder.getInstance().findNextFocus(),此处传入isRootNamespace()的ViewGroup和当前焦点(View)以及方向:
public final View findNextFocus(ViewGroup root, View focused, int direction) {
return findNextFocus(root, focused, null, direction);
}
private View findNextFocus(ViewGroup root, View focused, Rect focusedRect, int direction) {
View next = null;
if (focused != null) {
next = findNextUserSpecifiedFocus(root, focused, direction);
}
if (next != null) {
return next;
}
ArrayList<View> focusables = mTempList;
try {
focusables.clear();
root.addFocusables(focusables, direction);
if (!focusables.isEmpty()) {
next = findNextFocus(root, focused, focusedRect, direction, focusables);
}
} finally {
focusables.clear();
}
return next;
}
以上函数优先级顺序是:
a. 优先找开发者指定的下一个focus的view ,就是在xml或者代码中指定NextFocusDirection Id的view
b. 其次,根据算法去找,原理就是找在方向上最近的view
根据指定Id查找
从指定的FocusId查找,对应的函数为findNextUserSpecifiedFocus:
// FocusFinder.java
private View findNextUserSpecifiedFocus(ViewGroup root, View focused, int direction) {
// check for user specified next focus
View userSetNextFocus = focused.findUserSetNextFocus(root, direction);
if (userSetNextFocus != null && userSetNextFocus.isFocusable()
&& (!userSetNextFocus.isInTouchMode()
|| userSetNextFocus.isFocusableInTouchMode())) {
return userSetNextFocus;
}
return null;
}
先执行View的findUserSetNextFocus方法:
// View.java
View findUserSetNextFocus(View root, @FocusDirection int direction) {
switch (direction) {
case FOCUS_LEFT:
if (mNextFocusLeftId == View.NO_ID) return null;
return findViewInsideOutShouldExist(root, mNextFocusLeftId);
......
}
}
return null;
}
如上代码当按下左键,如果设置了mNextFocusLeftId,则会通过findViewInsideOutShouldExist去找这个View。 mNextFocusLeftId可以有两种方式设置: 一种是xml设置,比如:
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_1"
android:nextFocusLeft="@+id/btn_2"
... />
另一种是代码设置:
mBtn1.setNextFocusLeftId(R.id.btn_2);
具体findViewInsideOutShouldExist查询算法方法如下:
private View findViewInsideOutShouldExist(View root, int id) {
if (mMatchIdPredicate == null) {
mMatchIdPredicate = new MatchIdPredicate();
}
mMatchIdPredicate.mId = id;
View result = root.findViewByPredicateInsideOut(this, mMatchIdPredicate);
if (result == null) {
Log.w(VIEW_LOG_TAG, "couldn't find view with id " + id);
}
return result;
}
public final View findViewByPredicateInsideOut(View start, Predicate<View> predicate) {
View childToSkip = null;
for (;;) {
View view = start.findViewByPredicateTraversal(predicate, childToSkip);
if (view != null || start == this) {
return view;
}
ViewParent parent = start.getParent();
if (parent == null || !(parent instanceof View)) {
return null;
}
childToSkip = start;
start = (View) parent;
}
}
View的findViewByPredicateTraversal:
protected View findViewByPredicateTraversal(Predicate<View> predicate, View childToSkip) {
if (predicate.apply(this)) {
return this;
}
return null;
}
ViewGroup的findViewByPredicateTraversal:
protected View findViewByPredicateTraversal(Predicate<View> predicate, View childToSkip) {
if (predicate.apply(this)) {
return this;
}
final View[] where = mChildren;
final int len = mChildrenCount;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
View v = where[i];
if (v != childToSkip && (v.mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_IS_ROOT_NAMESPACE) == 0) {
v = v.findViewByPredicate(predicate);
if (v != null) {
return v;
}
}
}
return null;
}
view.findViewByPredicate:
public final View findViewByPredicate(Predicate<View> predicate) {
return findViewByPredicateTraversal(predicate, null);
}
可以看到,findViewInsideOutShouldExist这个方法从当前focused view去寻找指定id的view,findViewInsideOutShouldExist中调用的是root.findViewByPredicateInsideOut(this, mMatchIdPredicate);所以findViewByPredicateInsideOut的start参数是当前focused view,即从当前focused view开始向下遍历,如果没找到则从自己的parent开始向下遍历,直到找到id匹配的视图为止
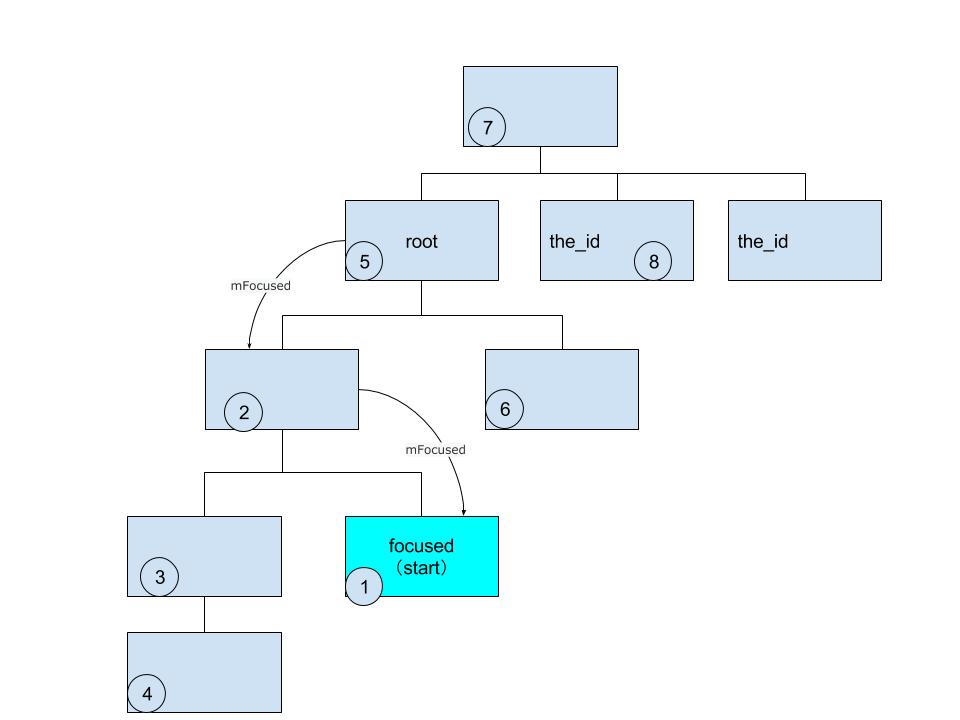
这里要注意的是,也许存在多个相同id的视图(比如ListView,RecyclerView,ViewPager等场景),但是这个方法只会返回在View树中节点范围最近的一个视图,这就是为什么有时候看似指定了focusId,但实际上焦点却丢失的原因,因为焦点跑到了另一个“意想不到”的相同id的视图上。
根据相对位置查找
如果开发者没有指定nextFocusId或查找失败,则根据相对位置找到指定方向上最近的View
try {
focusables.clear();
root.addFocusables(focusables, direction);
if (!focusables.isEmpty()) {
next = findNextFocus(root, focused, focusedRect, direction, focusables);
}
} finally {
focusables.clear();
}
return next;
首先查找出所有能获取焦点的View
//View.java
public void addFocusables(ArrayList<View> views, @FocusDirection int direction) {
addFocusables(views, direction, FOCUSABLES_TOUCH_MODE);
}
public void addFocusables(ArrayList<View> views, @FocusDirection int direction,
@FocusableMode int focusableMode) {
if (views == null) {
return;
}
if (!isFocusable()) {
return;
}
if ((focusableMode & FOCUSABLES_TOUCH_MODE) == FOCUSABLES_TOUCH_MODE
&& isInTouchMode() && !isFocusableInTouchMode()) {
return;
}
views.add(this);
}
对于View来说,如果能获取焦点则添加自己。
//ViewGroup.java
public void addFocusables(ArrayList<View> views, int direction, int focusableMode) {
final int focusableCount = views.size();
final int descendantFocusability = getDescendantFocusability();
if (descendantFocusability != FOCUS_BLOCK_DESCENDANTS) {
if (shouldBlockFocusForTouchscreen()) {
focusableMode |= FOCUSABLES_TOUCH_MODE;
}
final int count = mChildrenCount;
final View[] children = mChildren;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = children[i];
if ((child.mViewFlags & VISIBILITY_MASK) == VISIBLE) {
child.addFocusables(views, direction, focusableMode);
}
}
}
// we add ourselves (if focusable) in all cases except for when we are
// FOCUS_AFTER_DESCENDANTS and there are some descendants focusable. this is
// to avoid the focus search finding layouts when a more precise search
// among the focusable children would be more interesting.
if ((descendantFocusability != FOCUS_AFTER_DESCENDANTS
// No focusable descendants
|| (focusableCount == views.size())) &&
(isFocusableInTouchMode() || !shouldBlockFocusForTouchscreen())) {
super.addFocusables(views, direction, focusableMode);
}
}
对于ViewGroup来说,遍历并添加所有能获取焦点的child
这里有个descendantFocusability变量,有三个取值
- FOCUS_BEFORE_DESCENDANTS:在所有子视图之前获取焦点
- FOCUS_AFTER_DESCENDANTS: 在所有子视图之后获取焦点
- FOCUS_BLOCK_DESCENDANTS: 阻止所有子视图获取焦点,即使他们是focusable的
这里会根据descendantFocusability做相应处理,如果是FOCUS_BLOCK_DESCENDANTS将阻止子view获取焦点,则不遍历其子view。如果是FOCUS_AFTER_DESCENDANTS则会根据(focusableCount == views.size())判断子view有没有能focusable的,没有的话才可能将自己加到集合中。
从上面的逻辑看出direction在查找所有能focusable的view无任何作用。
找出所有能focusable的view后继续下一步查找:
private View findNextFocus(ViewGroup root, View focused, Rect focusedRect,
int direction, ArrayList<View> focusables) {
if (focused != null) {
if (focusedRect == null) {
focusedRect = mFocusedRect;
}
// fill in interesting rect from focused
focused.getFocusedRect(focusedRect);
root.offsetDescendantRectToMyCoords(focused, focusedRect);
} else {
if (focusedRect == null) {
focusedRect = mFocusedRect;
// make up a rect at top left or bottom right of root
switch (direction) {
case View.FOCUS_RIGHT:
case View.FOCUS_DOWN:
setFocusTopLeft(root, focusedRect);
break;
case View.FOCUS_FORWARD:
if (root.isLayoutRtl()) {
setFocusBottomRight(root, focusedRect);
} else {
setFocusTopLeft(root, focusedRect);
}
break;
case View.FOCUS_LEFT:
case View.FOCUS_UP:
setFocusBottomRight(root, focusedRect);
break;
case View.FOCUS_BACKWARD:
if (root.isLayoutRtl()) {
setFocusTopLeft(root, focusedRect);
} else {
setFocusBottomRight(root, focusedRect);
break;
}
}
}
}
switch (direction) {
case View.FOCUS_FORWARD:
case View.FOCUS_BACKWARD:
return findNextFocusInRelativeDirection(focusables, root, focused, focusedRect,
direction);
case View.FOCUS_UP:
case View.FOCUS_DOWN:
case View.FOCUS_LEFT:
case View.FOCUS_RIGHT:
return findNextFocusInAbsoluteDirection(focusables, root, focused,
focusedRect, direction);
default:
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unknown direction: " + direction);
}
}
从上面代码看出是先找出参照区域,然后根据参照区域和相对位置找出下一个focus view
如果当前焦点view不为空,则先获取当前focused view相对root view的相对区域坐标,包含left,top,right,bottom算法如下:
focused.getFocusedRect(focusedRect);
root.offsetDescendantRectToMyCoords(focused,focusedRect);
//View.java
public void getFocusedRect(Rect r) {
getDrawingRect(r);
}
//ViewGroup.java
public final void offsetDescendantRectToMyCoords(View descendant, Rect rect) {
offsetRectBetweenParentAndChild(descendant, rect, true, false);
}
void offsetRectBetweenParentAndChild(View descendant, Rect rect,
boolean offsetFromChildToParent, boolean clipToBounds) {
// already in the same coord system :)
if (descendant == this) {
return;
}
ViewParent theParent = descendant.mParent;
// search and offset up to the parent
while ((theParent != null)
&& (theParent instanceof View)
&& (theParent != this)) {
if (offsetFromChildToParent) {
rect.offset(descendant.mLeft - descendant.mScrollX,
descendant.mTop - descendant.mScrollY);
if (clipToBounds) {
View p = (View) theParent;
rect.intersect(0, 0, p.mRight - p.mLeft, p.mBottom - p.mTop);
}
} else {
if (clipToBounds) {
View p = (View) theParent;
rect.intersect(0, 0, p.mRight - p.mLeft, p.mBottom - p.mTop);
}
rect.offset(descendant.mScrollX - descendant.mLeft,
descendant.mScrollY - descendant.mTop);
}
descendant = (View) theParent;
theParent = descendant.mParent;
}
// now that we are up to this view, need to offset one more time
// to get into our coordinate space
if (theParent == this) {
if (offsetFromChildToParent) {
rect.offset(descendant.mLeft - descendant.mScrollX,
descendant.mTop - descendant.mScrollY);
} else {
rect.offset(descendant.mScrollX - descendant.mLeft,
descendant.mScrollY - descendant.mTop);
}
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("parameter must be a descendant of this view");
}
}
以上算法中offsetFromChildToParent=true,clipToBounds=false。计算子view相对root view的坐标位置。
如果当前没有焦点view,以右键和下键为例,调用的方法如下:
private void setFocusTopLeft(ViewGroup root, Rect focusedRect) {
final int rootTop = root.getScrollY();
final int rootLeft = root.getScrollX();
focusedRect.set(rootLeft, rootTop, rootLeft, rootTop);
}
即如果当前没有焦点view,当按下右键和下键以root view的左上角的点为参照计算。
然后继续查找: 如果方向是View.FOCUS_FORWARD和View.FOCUS_BACKWARD,则根据相对位置来查找。
private View findNextFocusInRelativeDirection(ArrayList<View> focusables, ViewGroup root,
View focused, Rect focusedRect, int direction) {
try {
// Note: This sort is stable.
mSequentialFocusComparator.setRoot(root);
mSequentialFocusComparator.setIsLayoutRtl(root.isLayoutRtl());
Collections.sort(focusables, mSequentialFocusComparator);
} finally {
mSequentialFocusComparator.recycle();
}
final int count = focusables.size();
switch (direction) {
case View.FOCUS_FORWARD:
return getNextFocusable(focused, focusables, count);
case View.FOCUS_BACKWARD:
return getPreviousFocusable(focused, focusables, count);
}
return focusables.get(count - 1);
}
首先是将所有能获取焦点的View列表focusables进行重排序,排序算法
public int compare(View first, View second) {
if (first == second) {
return 0;
}
getRect(first, mFirstRect);
getRect(second, mSecondRect);
if (mFirstRect.top < mSecondRect.top) {
return -1;
} else if (mFirstRect.top > mSecondRect.top) {
return 1;
} else if (mFirstRect.left < mSecondRect.left) {
return mIsLayoutRtl ? 1 : -1;
} else if (mFirstRect.left > mSecondRect.left) {
return mIsLayoutRtl ? -1 : 1;
} else if (mFirstRect.bottom < mSecondRect.bottom) {
return -1;
} else if (mFirstRect.bottom > mSecondRect.bottom) {
return 1;
} else if (mFirstRect.right < mSecondRect.right) {
return mIsLayoutRtl ? 1 : -1;
} else if (mFirstRect.right > mSecondRect.right) {
return mIsLayoutRtl ? -1 : 1;
} else {
// The view are distinct but completely coincident so we consider
// them equal for our purposes. Since the sort is stable, this
// means that the views will retain their layout order relative to one another.
return 0;
}
}
先将View坐标转换成Root view对应的坐标,让后根据top>left>bottom>right优先级排序。
private static View getNextFocusable(View focused, ArrayList<View> focusables, int count) {
if (focused != null) {
int position = focusables.lastIndexOf(focused);
if (position >= 0 && position + 1 < count) {
return focusables.get(position + 1);
}
}
if (!focusables.isEmpty()) {
return focusables.get(0);
}
return null;
}
然后获取当前focused 在列表中的位置,获取下一个焦点view。 从以上算法函数实现可以看出并没有使用到之前计算出来的当前focused相对矩形区域focusedRect
如果是上下左右的方位则使用绝对方位查找:
View findNextFocusInAbsoluteDirection(ArrayList<View> focusables, ViewGroup root, View focused,
Rect focusedRect, int direction) {
// initialize the best candidate to something impossible
// (so the first plausible view will become the best choice)
mBestCandidateRect.set(focusedRect);
switch(direction) {
case View.FOCUS_LEFT:
mBestCandidateRect.offset(focusedRect.width() + 1, 0);
break;
case View.FOCUS_RIGHT:
mBestCandidateRect.offset(-(focusedRect.width() + 1), 0);
break;
case View.FOCUS_UP:
mBestCandidateRect.offset(0, focusedRect.height() + 1);
break;
case View.FOCUS_DOWN:
mBestCandidateRect.offset(0, -(focusedRect.height() + 1));
}
View closest = null;
int numFocusables = focusables.size();
for (int i = 0; i < numFocusables; i++) {
View focusable = focusables.get(i);
// only interested in other non-root views
if (focusable == focused || focusable == root) continue;
// get focus bounds of other view in same coordinate system
focusable.getFocusedRect(mOtherRect);
root.offsetDescendantRectToMyCoords(focusable, mOtherRect);
if (isBetterCandidate(direction, focusedRect, mOtherRect, mBestCandidateRect)) {
mBestCandidateRect.set(mOtherRect);
closest = focusable;
}
}
return closest;
}
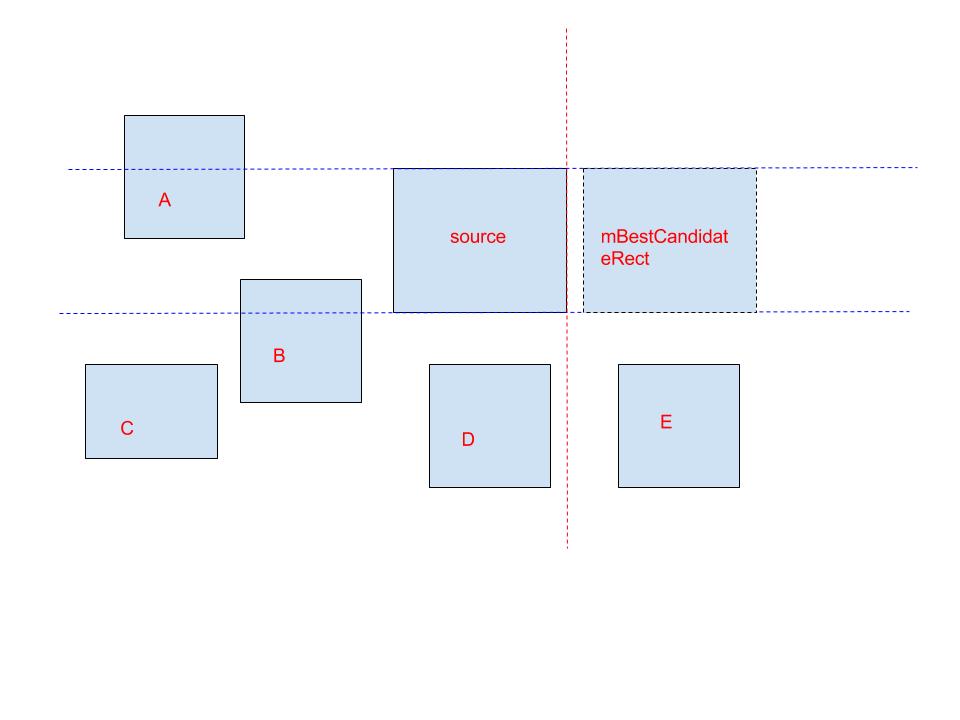
先获取最佳子View的矩形区域mBestCandidateRect。mBestCandidateRect是无效区域最接近focusedRect的矩形。然后遍历focusables列表,根据算法找到最佳的子view。
最佳子view算法:
boolean isBetterCandidate(int direction, Rect source, Rect rect1, Rect rect2) {
// to be a better candidate, need to at least be a candidate in the first
// place :)
if (!isCandidate(source, rect1, direction)) {
return false;
}
// we know that rect1 is a candidate.. if rect2 is not a candidate,
// rect1 is better
if (!isCandidate(source, rect2, direction)) {
return true;
}
// if rect1 is better by beam, it wins
if (beamBeats(direction, source, rect1, rect2)) {
return true;
}
// if rect2 is better, then rect1 cant' be :)
if (beamBeats(direction, source, rect2, rect1)) {
return false;
}
// otherwise, do fudge-tastic comparison of the major and minor axis
return (getWeightedDistanceFor(
majorAxisDistance(direction, source, rect1),
minorAxisDistance(direction, source, rect1))
< getWeightedDistanceFor(
majorAxisDistance(direction, source, rect2),
minorAxisDistance(direction, source, rect2)));
}
下面用View.FOCUS_LEFT举例说明:
- 先排除focused 右边的view
- 判断下一个view和当前最佳view是否和source是否有重叠,这个重叠指高度是否有重叠。如果都重叠或都不中重叠,则根据距离判断是否更优
- 如果一个有重叠一个没有重叠,如果是左右方向则重叠的view更优,如果是上下方向,则还需进一步比较距离。
小结
经过对源码的分析,系统本身寻找下一个焦点视图的过程是:
- 首先寻找用户指定了id的视图,从当前焦点视图的节点开始遍历,直到找到匹配该id的视图。也许存在多个相同id的视图,但是只会找到视图节点树中最近的一个。
- 如果没有指定id,则遍历找出所有isFocusable的视图,统一坐标系,然后计算出指定方向上离当前焦点视图最近的一个视图。
结合KeyEvent事件的流转,处理焦点的时机,按照优先级(顺序)依次是:
- dispatchKeyEvent
- mOnKeyListener.onKey
- onKeyDown/onKeyUp
- focusSearch
- 指定nextFocusId
- 系统自动从所有isFocusable的视图中找下一个焦点视图
自定义按键焦点实现
方案分析
需求:当只有左右按键(或其他键值)时,实现界面按键循环选择
按照上面源码分析可知,如果按照android默认的实现,左右按键只能在左右两个方向处理焦点,不会处理上下方向的焦点,但是目前需要能循环处理焦点。 需找到方法改变按键的方向,使其按照指定的方向查找下一个焦点。
目前想到可能的方式:
- 重载 dispatchKeyEvent,根据按键键值处理
- 重载 onKeyDown/onKeyUp,根据按键键值处理
- 重载 focusSearch
- 布局中指定nextFocusId
可以想象到: 使用第1,2种方后自己需要做很多事情:判断键值,找下一个焦点View,处理焦点状态,如果是列表还需要滑动,需要把系统中一些默认实现再实现一遍。 如果使用第4种方式,focuseable的View都需要定义id,而且每个view还要设置nextFocusLeft和nextFocusRight,非常繁琐且定义好的id不方便修改。
重载focusSearch是最好的选择。其函数声明public View focusSearch(View focused, int direction)第二个参数是int型的方向值,可以很方便的随意改变,而且可以看到View.FOCUS_FORWARD,View.FOCUS_BACKWARD两种方向的查询是将view按位置从上到下,从左到右排序后查询,实际上就是循环查询。
以下寻找能方便使用focusSearch的原生控件
原生控件选择
根据上面焦点处理过程,寻找能调用到focusSearch的控件。因此控件不能重载dispatchKeyEvent, mOnKeyListener.onKey, onKeyDown/onKeyUp方法。
ListView
@Override
public boolean onKeyDown(int keyCode, KeyEvent event) {
return commonKey(keyCode, 1, event);
}
@Override
public boolean onKeyMultiple(int keyCode, int repeatCount, KeyEvent event) {
return commonKey(keyCode, repeatCount, event);
}
@Override
public boolean onKeyUp(int keyCode, KeyEvent event) {
return commonKey(keyCode, 1, event);
}
ListView重写了以上方法,舍弃
RecyclerView
@Override
public View focusSearch(View focused, int direction) {
View result = mLayout.onInterceptFocusSearch(focused, direction);
if (result != null) {
return result;
}
final FocusFinder ff = FocusFinder.getInstance();
result = ff.findNextFocus(this, focused, direction);
if (result == null && mAdapter != null && mLayout != null) {
eatRequestLayout();
result = mLayout.onFocusSearchFailed(focused, direction, mRecycler, mState);
resumeRequestLayout(false);
}
return result != null ? result : super.focusSearch(focused, direction);
}
很幸运RecyclerView只重载了focusSearch,可以替代listView。
ScrollView
@Override
public boolean dispatchKeyEvent(KeyEvent event) {
// Let the focused view and/or our descendants get the key first
return super.dispatchKeyEvent(event) || executeKeyEvent(event);
}
很不幸,不能愉快的使用ScrollView
其他
mFocused
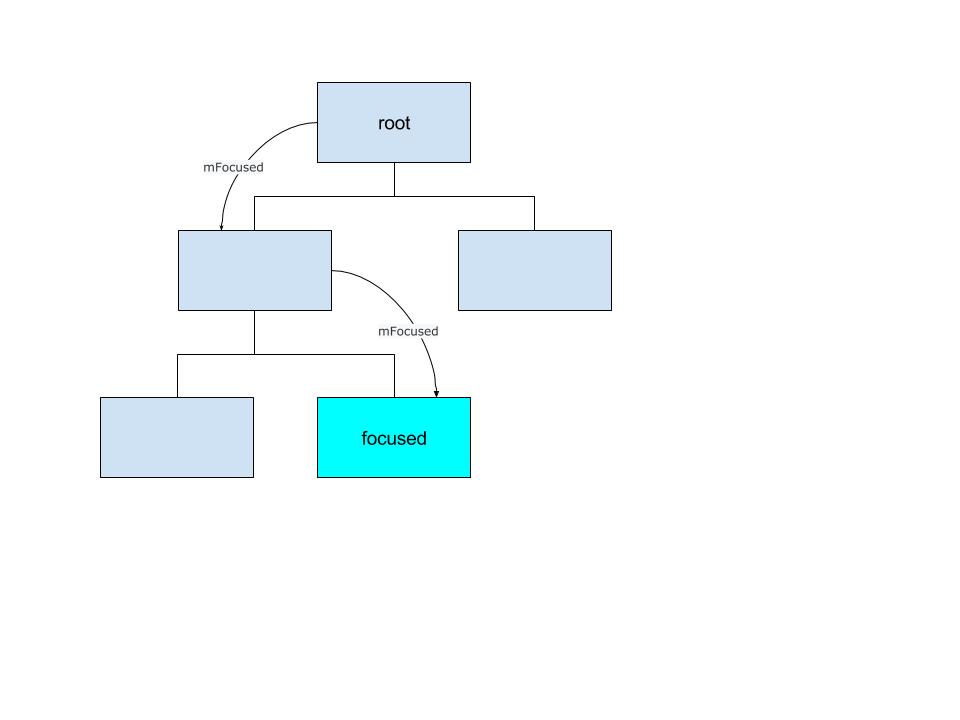 mFocused一般通过View.requestFocus获取焦点,最终调用ViewGroup.requestChildFocus()方法获取:
mFocused一般通过View.requestFocus获取焦点,最终调用ViewGroup.requestChildFocus()方法获取:
//View.java
private boolean requestFocusNoSearch(int direction, Rect previouslyFocusedRect) {
// need to be focusable
if ((mViewFlags & FOCUSABLE_MASK) != FOCUSABLE ||
(mViewFlags & VISIBILITY_MASK) != VISIBLE) {
return false;
}
// need to be focusable in touch mode if in touch mode
if (isInTouchMode() &&
(FOCUSABLE_IN_TOUCH_MODE != (mViewFlags & FOCUSABLE_IN_TOUCH_MODE))) {
return false;
}
// need to not have any parents blocking us
if (hasAncestorThatBlocksDescendantFocus()) {
return false;
}
handleFocusGainInternal(direction, previouslyFocusedRect);
return true;
}
void handleFocusGainInternal(@FocusRealDirection int direction, Rect previouslyFocusedRect) {
if (DBG) {
System.out.println(this + " requestFocus()");
}
if ((mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_FOCUSED) == 0) {
mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_FOCUSED;
View oldFocus = (mAttachInfo != null) ? getRootView().findFocus() : null;
if (mParent != null) {
mParent.requestChildFocus(this, this);
}
if (mAttachInfo != null) {
mAttachInfo.mTreeObserver.dispatchOnGlobalFocusChange(oldFocus, this);
}
onFocusChanged(true, direction, previouslyFocusedRect);
refreshDrawableState();
}
}
//ViewGroup.java
public void requestChildFocus(View child, View focused) {
if (DBG) {
System.out.println(this + " requestChildFocus()");
}
if (getDescendantFocusability() == FOCUS_BLOCK_DESCENDANTS) {
return;
}
// Unfocus us, if necessary
super.unFocus(focused);
// We had a previous notion of who had focus. Clear it.
if (mFocused != child) {
if (mFocused != null) {
mFocused.unFocus(focused);
}
mFocused = child;
}
if (mParent != null) {
mParent.requestChildFocus(this, focused);
}
}
mParent
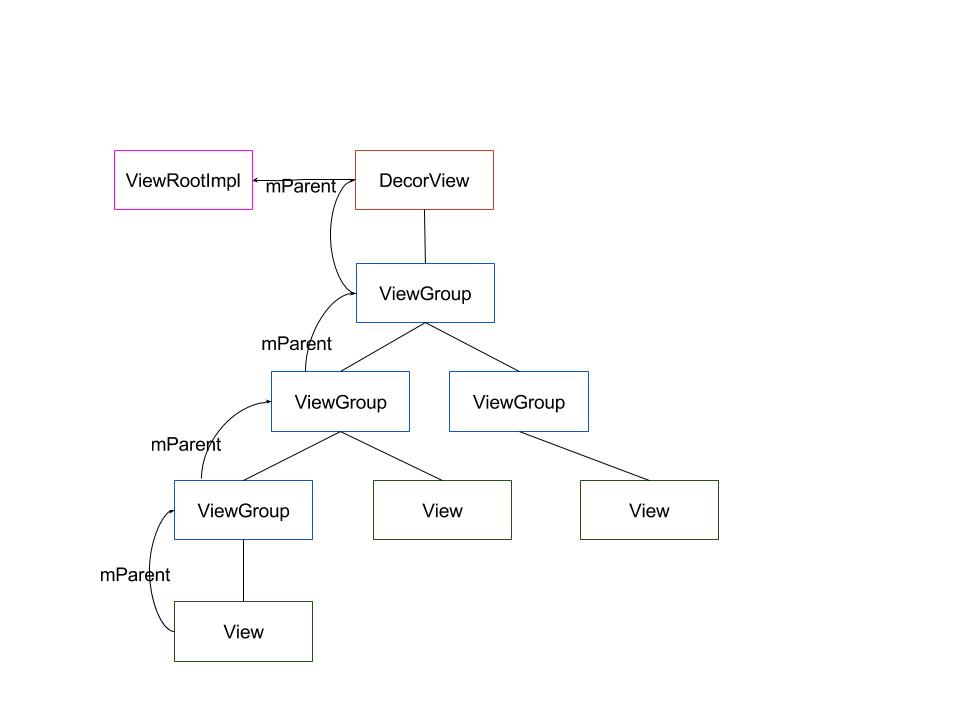
参考:
- Android 5.1.1源码
- http://blog.csdn.net/archer_zoro/article/details/60605578